There are many steps involved when developing guidelines with engagement from a variety of different stakeholders. They are developed by multidisciplinary committees that follow a rigorous evidence-based approach. They are informed by the judgement of evidence by experts, and the views of consumers, community groups and other people affected by the guidelines.
This detailed process has been outlined in the flow diagram.
Flow diagram: Developing NHMRC guidelines or advice
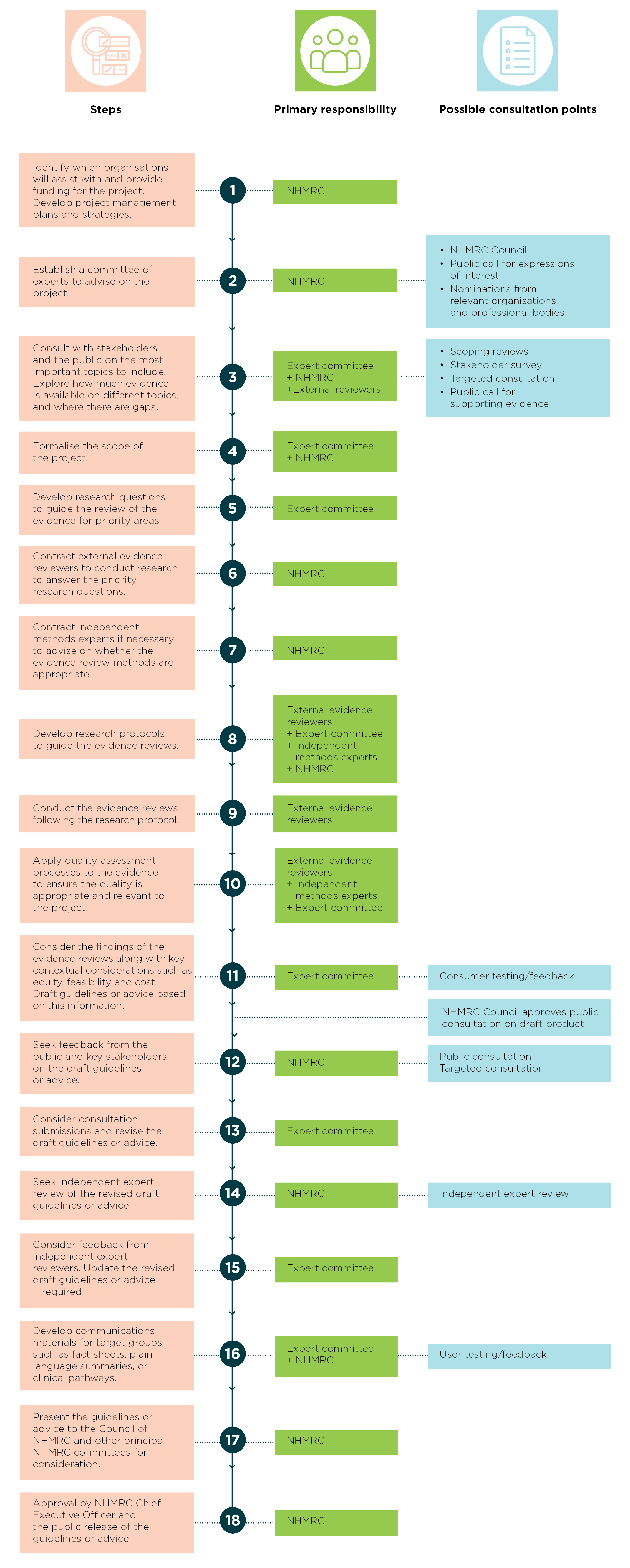
- Image description - Flow diagram
Step 1: Identify which organisations will assist with and provide funding for the project. Develop project management plans and strategies.
- Primary responsibility: NHMRC
Step 2: Establish a committee of experts to advise on the project.
- Primary responsibility: NHMRC
- Possible consultation points: NHMRC Council, public call for expressions of interest, nominations from relevant organisations and professional bodies.
Step 3: Consult with stakeholders and the public on the most important topics to include. Explore how much evidence is available on different topics, and where there are gaps.
- Primary responsibility: Expert committee + NHMRC + External reviewers
- Possible consultation points: Scoping reviews, stakeholder survey, targeted consultation, public call for supporting evidence.
Step 4: Formalise the scope of the project.
- Primary responsibility: Expert committee, NHMRC
Step 5: Develop research questions to guide the review of the evidence for priority areas.
- Primary responsibility: Expert committee
Step 6: Contract external evidence reviewers to conduct research to answer the priority research questions.
- Primary responsibility: NHMRC
Step 7: Contract independent methods experts if necessary to advise on whether the evidence review methods are appropriate.
- Primary responsibility: NHMRC
Step 8: Develop research protocols to guide the evidence reviews.
- Primary responsibility: External evidence reviewers, Expert committee, independent methods experts, NHMRC
Step 9: Conduct the evidence reviews following the research protocol.
- Primary responsibility: External evidence reviewers
Step 10: Apply quality assessment processes to the evidence to ensure the quality is appropriate and relevant to the project.
- Primary responsibility: External evidence reviewers, Independent methods experts, Expert committee
Step 11: Consider the findings of the evidence reviews along with key contextual considerations such as equity, feasibility and cost. Draft guidelines or advice based on this information.
- Primary responsibility: Expert committee
- Possible consultation points: Consumer testing/feedback
- NHMRC Council approves public consultation on draft product.
Step 12: Seek feedback from the public and key stakeholders on the draft guidelines or advice.
- Primary responsibility: NHMRC
- Possible consultation points: Public consultation, Targeted consultation
Step 13: Consider consultation submissions and revise the draft guidelines or advice.
- Primary responsibility: Expert committee
Step 14: Seek independent expert review of the revised draft guidelines or advice.
- Primary responsibility: NHMRC
- Possible consultation points: Independent expert review
Step 15: Consider feedback from independent expert reviewers. Update the revised draft guidelines or advice if required.
- Primary responsibility: Expert committee
Step 16: Develop communications materials for target groups such as fact sheets, plain language summaries, or clinical pathways.
- Primary responsibility: Expert committee + NHMRC
- Possible consultation points: User testing/feedback
Step 17: Present the guidelines or advice to the Council of NHMRC and other principal NHMRC committees for endorsement.
- Primary responsibility: NHMRC
Step 18: Approval by NHMRC Chief Executive Officer and the public release of the guidelines or advice.
- Primary responsibility: NHMRC
Processes used to develop clinical and public health guidelines can often vary depending on the available resources, nature of the evidence and the needs of the audience. NHMRC publishes detailed records of decisions and judgements made during the development process to ensure transparency.